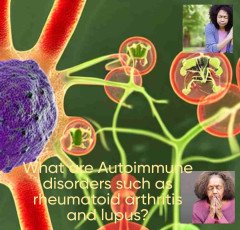
What are Autoimmune disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus ?

The body's immune system mistakenly assaults healthy cells and tissues in autoimmune illnesses including lupus and rheumatoid arthritis.
Immune cells that are part of a healthy immune system fight foreign substances including viruses, bacteria, and cancer cells; however, immune cells that are part of autoimmune illnesses attack the body's own cells.
The immune system destroys the lining of the joints in rheumatoid arthritis, resulting in swelling, discomfort, and stiffness.
In lupus, the immune system can attack the skin, joints, kidneys, brain, and other organs. As a result, a variety of symptoms, including joint pain, skin rashes, exhaustion, and fever, can occur.
Genetics, environmental triggers, anomalies in the immune system, and other complicated factors can all play a role in autoimmune illnesses.
Although there is presently no treatment for autoimmune illnesses, there are methods to control symptoms and halt the disease's progression.
Anti-inflammatory medications, corticosteroids, and disease-modifying antirheumatic medicines (DMARDs) are a few of the main treatments for autoimmune illnesses.
These drugs can lessen discomfort and inflammation while also delaying the onset of the disease.
For those with autoimmune illnesses, lifestyle modifications can help manage symptoms and enhance general health in addition to drugs.
This might entail a balanced diet, frequent exercise, stress reduction methods, and adequate rest.
Developing a specialized treatment strategy requires close collaboration between autoimmune illness sufferers and their medical professionals.
Regular examinations and monitoring can verify that the course of treatment is effective and modified as necessary.
Even though autoimmune illnesses can be difficult to treat, many people can enjoy active, fulfilling lives with the correct support and care.
A person with an autoimmune disorder should be aware of any potential consequences that can result from their illness.
For instance, persons with lupus may have a higher risk of renal damage, but people with rheumatoid arthritis may have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
People with autoimmune illnesses can benefit from routine monitoring and care of these potential consequences because it can help stop further harm and enhance outcomes.
The goal of current research is to comprehend autoimmune diseases better and create innovative treatments.
These might include gene therapy and other novel therapies, as well as biologic medications that target certain immune system organs.
Although managing autoimmune illnesses can be difficult, many people can lead active, fulfilling lives with the correct support and care.
It's crucial to speak with your healthcare practitioner if you are exhibiting signs of an autoimmune condition in order to identify the underlying issue and create a suitable treatment strategy.
It's crucial to remember that autoimmune diseases can significantly affect a person's emotional and mental health.
Many people with autoimmune disorders may develop anxiety, sadness, or other mental health issues because treating symptoms and coping with chronic illness can be demanding and exhausting.
People with autoimmune diseases should look for assistance and tools to manage their emotional and mental health. This could entail counseling, support groups, or other types of mental health care.
Support and encouragement from family members and caregivers of those with autoimmune diseases can be very helpful. They can offer emotional support, assistance with everyday duties, and guidance within the healthcare system.
Complex diseases like autoimmune disorders call for continuing management and care.
But many people with autoimmune diseases may control their symptoms and live happy, fulfilling lives with the correct care and assistance.
It's also important to remember that people of different ages, genders, and socioeconomic backgrounds can develop autoimmune illnesses.
Some autoimmune diseases affect both sexes equally, whereas others are more common in women than in males.
There may be a hereditary component to some autoimmune illnesses since they may run in families.
Additionally, some environmental elements may cause or worsen autoimmune diseases.
Infections, exposure to specific poisons or chemicals, or even stress, may be among them. On the other hand, the precise causes and processes of autoimmune illnesses are still poorly known.
As a result, it's not always possible to prevent autoimmune diseases.
However, making efforts to maintain general health and wellbeing may boost the immune system and lessen the risk of developing specific autoimmune illnesses. These efforts can include getting adequate sleep, eating a good diet, and decreasing stress.
It's crucial to get medical care as soon as you can if you think you might have an autoimmune condition.
The progression of the disease can be slowed down and outcomes can be improved with early identification and therapy.









 All Wireless Products
All Wireless Products  The Click Engine
The Click Engine  NordPass
NordPass  NordVPN
NordVPN  1150+Trendy kids coloring pages Bundle
1150+Trendy kids coloring pages Bundle  ASUS Laptop
ASUS Laptop  NordLocker
NordLocker  One World Collection
One World Collection  Graphics & Design
Graphics & Design  The Secret Email System
The Secret Email System  ASPINAL LONDON
ASPINAL LONDON  RPM 3.0
RPM 3.0  Favorite Company (Cuelinks)
Favorite Company (Cuelinks)  Unlimited access to classes on illustration, photography, design, film, music
Unlimited access to classes on illustration, photography, design, film, music  Women Fashion
Women Fashion  Best Robotic Vacuum Cleaners
Best Robotic Vacuum Cleaners  Sennheiser
Sennheiser  Best Selling Books
Best Selling Books  SOFAS
SOFAS  Unreal Engine 5 For Beginners Learn The Basics Of Virtual Production
Unreal Engine 5 For Beginners Learn The Basics Of Virtual Production  Amazon Best Selling Products
Amazon Best Selling Products  ELECTRONIC ACCESSORIES
ELECTRONIC ACCESSORIES  Online Technology Classes
Online Technology Classes  Creative Brief For Video Shoot
Creative Brief For Video Shoot  BEST SELLER TOP10
BEST SELLER TOP10  TitTok Revolution
TitTok Revolution  Men Clothing
Men Clothing  Best Sellers On Amazon
Best Sellers On Amazon  Online Marketing
Online Marketing  SEO Checklist
SEO Checklist  Best Home Appliances
Best Home Appliances  Only For The United States
Only For The United States  Acer Laptop
Acer Laptop  Hot Bags For Pain Relief
Hot Bags For Pain Relief  Top Rated From Amazon
Top Rated From Amazon  Hello Theme
Hello Theme  Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence  Smart Doorbell
Smart Doorbell 
















