
Occupational Diseases And Exposures

Health disorders that are brought on by exposure to specific hazardous substances or working conditions are referred to as occupational diseases and exposures. The lungs, skin, eyes, and other organs can all be impacted by these illnesses.
The following are some instances of occupational illnesses and exposures:
Employers are responsible for ensuring a safe and healthy work environment, which includes limiting employee exposure to potentially dangerous substances and environments.
Additionally, it is crucial that employees take action to safeguard themselves, including donning personal protective equipment and adhering to the correct safety protocols.
The health and wellbeing of workers can be significantly impacted by occupational diseases and exposures, which can result in disability, lost pay, and in some cases, even death. Financial effects from these conditions may be felt by the worker, their family, and the healthcare system.
Protecting workers and fostering a healthy work environment both depend on preventing occupational diseases and exposures.
Employers can take the following actions to stop these conditions:
By adhering to safety guidelines, employing personal protective equipment, notifying their employer of risks or hazardous circumstances, and seeking medical assistance if they experience signs of a work-related sickness or injury, employees can also help to prevent occupational diseases and exposures.
Overall, maintaining worker health and safety as well as the long-term viability of enterprises and sectors depends on preventing occupational diseases and exposures.
Many nations have laws and rules requiring firms to give their workers a safe and healthy work environment.
In order to prevent occupational diseases and exposures, these regulations may stipulate requirements for hazard identification and assessment, safety training, personal protective equipment, medical monitoring, and other preventative measures. Employers who break these regulations may be subject to fines, penalties, or other legal repercussions.
Employees may be entitled to compensation, such as workers' compensation or disability payments, if they contract an occupational sickness or are exposed to it. In some circumstances, employees can also be entitled to sue their employer if they can demonstrate that the company failed to safeguard them against occupational dangers.
In addition to physical risks, the workplace also presents psychological risks that can result in stress, anxiety, and other mental health issues.
Workplace bullying, harassment, or exposure to traumatic situations are a few examples of these dangers. All employees must work in a safe and healthy environment, which is the responsibility of the employer.
Occupational diseases and exposures are medical disorders brought on by being exposed to potentially harmful elements at work.
To safeguard the health and safety of employees as well as the long-term viability of enterprises and industries, these circumstances must be avoided. There are laws and regulations in place to guarantee that employers follow them. Employers and employees both have a role to play in reducing occupational diseases and exposures.
To note that some industries are more likely than others to have occupational illnesses and exposures. For instance, employees in the construction, farming, mining, and healthcare industries are more likely to be exposed to hazardous materials and working conditions. Employers in these businesses must emphasize safety and put in place practical safeguards to protect their employees because these workers may be at higher risk of suffering work-related illnesses or accidents.
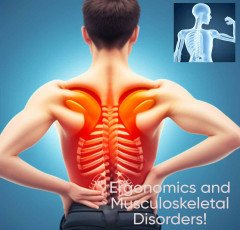
Additionally, if new technology and working conditions change, new dangers might potentially appear. For instance, long-term computer users run the risk of developing musculoskeletal conditions like carpal tunnel syndrome or neck and shoulder pain. Employers must be on guard, evaluate the dangers brought on by new technologies and working methods, and take action to reduce those risks.
The wider community is just as responsible as employers and employees for preventing occupational diseases and exposures.
Governmental organizations, for instance, can assist by enforcing worker protection rules and regulations and by financing studies into the health impacts of occupational dangers. Employers can be screened for occupational illnesses by healthcare experts as another way to contribute.
To preserve the health and safety of employees, it is essential to prevent occupational diseases and exposures, and many parties are involved in providing a safe and healthy workplace. Employers, employees, governmental organizations, and healthcare professionals may all work together to prevent these problems and develop a workplace that is safer and healthier for everyone.
Noting that occupational illnesses and exposures can have a considerable financial impact on people, employers, and society at large.
There are indirect costs as well, such as decreased productivity, increased absenteeism, and the expense of training and replacing people who are unable to work due to occupational diseases and exposures, in addition to the direct costs linked to medical care, lost income, and disability.
Therefore, it is morally and ethically fair to invest in prevention strategies to lower the prevalence of occupational diseases and exposures, and it also makes sound financial sense. Employers may enhance the health and wellbeing of their workforce, lower the expenses associated with occupational injuries and illnesses, and boost their bottom line by putting effective preventative measures in place.
A serious public health concern that affects millions of employees globally are occupational illnesses and exposures.
It takes a concerted effort from all parties involved to prevent these illnesses, including companies, employees, governmental organizations, and healthcare practitioners. Together, we can make workplaces safer and healthier while lowering the prevalence of occupational illnesses and exposures.
It's important to note that protecting against occupational illnesses and exposures is crucial from both an environmental and human health and economic standpoint. Chemicals and hazardous waste are only two examples of the many things and situations that can lead to occupational diseases and exposures.
We can lessen the negative effects of these substances and situations on the environment by taking steps to minimize occupational diseases and exposures, such as minimizing the use of hazardous chemicals and appropriately disposing of hazardous waste. This can therefore result in a safer and more environmentally friendly workplace, as well as a healthier atmosphere for everyone.
Not only is it crucial for the long-term sustainability of enterprises and industries, but also for the environment and the health and safety of workers, to prevent occupational diseases and exposures. Together, we can minimize the prevalence of occupational diseases and exposures, establish safer and better working conditions, and safeguard the environment for coming generations.














 Best Selling Books
Best Selling Books  BEST SELLER TOP10
BEST SELLER TOP10  Smart Doorbell
Smart Doorbell  Online Technology Classes
Online Technology Classes  Hot Bags For Pain Relief
Hot Bags For Pain Relief  One World Collection
One World Collection  ASPINAL LONDON
ASPINAL LONDON  Online Marketing
Online Marketing  All Wireless Products
All Wireless Products  Women Fashion
Women Fashion  1150+Trendy kids coloring pages Bundle
1150+Trendy kids coloring pages Bundle  Sennheiser
Sennheiser  Hello Theme
Hello Theme  NordLocker
NordLocker  SOFAS
SOFAS  Only For The United States
Only For The United States  Favorite Company (Cuelinks)
Favorite Company (Cuelinks)  Acer Laptop
Acer Laptop  Best Robotic Vacuum Cleaners
Best Robotic Vacuum Cleaners  NordVPN
NordVPN  Top Rated From Amazon
Top Rated From Amazon  Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence  Best Sellers On Amazon
Best Sellers On Amazon  Amazon Best Selling Products
Amazon Best Selling Products  SEO Checklist
SEO Checklist  The Secret Email System
The Secret Email System  Best Home Appliances
Best Home Appliances  ASUS Laptop
ASUS Laptop  Unlimited access to classes on illustration, photography, design, film, music
Unlimited access to classes on illustration, photography, design, film, music  Creative Brief For Video Shoot
Creative Brief For Video Shoot  NordPass
NordPass  Men Clothing
Men Clothing  Unreal Engine 5 For Beginners Learn The Basics Of Virtual Production
Unreal Engine 5 For Beginners Learn The Basics Of Virtual Production  TitTok Revolution
TitTok Revolution  The Click Engine
The Click Engine  RPM 3.0
RPM 3.0  ELECTRONIC ACCESSORIES
ELECTRONIC ACCESSORIES  Graphics & Design
Graphics & Design 
















