
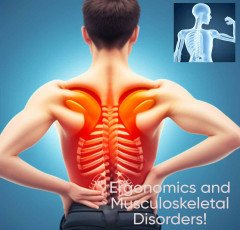
Occupational Stress And Burnout

Occupational stress is the term used to describe the unfavorable mental and physical reactions that might happen when someone believes that the demands of their
job are greater than their capacity to handle them. Numerous symptoms, such as anxiety, depression, irritability, and physical health issues, might result from this.
On the other side, burnout is a condition of physical, mental, and emotional weariness brought on by extended exposure to persistent work stress.
It is characterized by a diminished sense of accomplishment, cynicism, and emotions of detachment. Effective job performance can be impacted by burnout, which can also have a detrimental impact on a person's relationships and personal life.
Heavy workloads, a lack of control over one's professional responsibilities, a lack of support from coworkers or bosses, and emotionally taxing employment or work that frequently involves interpersonal conflict are some prominent causes of occupational stress and burnout. Burnout and occupational stress can be avoided and reduced by addressing these variables with good management and support.
Burnout and workplace stress can have detrimental effects on people, businesses, and society as a whole.
Burnout can have negative effects on a person's physical and emotional health as well as their productivity, absenteeism, and turnover rates. Employers may incur more costs as a result, while clients or customers may receive care that is of lower quality.
To avoid and treat occupational stress and burnout, a number of measures can be adopted.
One important strategy is to establish a welcoming workplace that promotes candid communication, teamwork, and a pleasant work culture. This can entail creating opportunity for professional growth, flexible work schedules, and access to tools like counseling and wellness initiatives.
Additionally, people can take action to control their own stress levels and avoid burnout. Setting achievable objectives, prioritizing self-care practices like exercise and mindfulness, and asking for help from coworkers, friends, and family are a few examples of how to do this.
It's critical to address workplace stress and burnout if you want to foster people's wellbeing and develop wholesome, effective work environments.
Organizations may increase employee satisfaction, productivity, and overall success by taking proactive measures to prevent and manage these challenges.
There are various therapies that have been shown to be useful in avoiding or treating occupational stress and burnout in addition to the already stated measures. For instance, cognitive-behavioral treatment (CBT) has been proven to be successful in lowering occupational stress and burnout in other occupational groups, including healthcare professionals.
Stress reduction and avoidance of burnout have both been linked to mindfulness-based therapies.
These interventions concentrate on honing mindfulness meditation techniques, which involve being conscious of the current moment without passing judgment. A variety of populations, including healthcare professionals, have shown that mindfulness is useful in lowering stress and enhancing general well-being.
Promoting a feeling of meaning and purpose in people's work is another strategy for minimizing burnout.
This may entail assisting people in making a connection with the organization's overarching objective and in realizing the effects of their work on other people. It may also entail offering chances for recognition and awards, as well as for professional and personal development.
Should understand that burnout and professional stress are complicated issues driven by a range of societal, organizational, and human factors. In order to address these problems, a multifaceted strategy that supports healthy work environments and work-life balance must be used. This strategy should include both individual and organizational interventions.














 The Secret Email System
The Secret Email System  One World Collection
One World Collection  NordPass
NordPass  Best Sellers On Amazon
Best Sellers On Amazon  Graphics & Design
Graphics & Design  Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence  All Wireless Products
All Wireless Products  Sennheiser
Sennheiser  Best Selling Books
Best Selling Books  Women Fashion
Women Fashion  1150+Trendy kids coloring pages Bundle
1150+Trendy kids coloring pages Bundle  Acer Laptop
Acer Laptop  Best Home Appliances
Best Home Appliances  BEST SELLER TOP10
BEST SELLER TOP10  Online Marketing
Online Marketing  Hot Bags For Pain Relief
Hot Bags For Pain Relief  RPM 3.0
RPM 3.0  ASPINAL LONDON
ASPINAL LONDON  SOFAS
SOFAS  Amazon Best Selling Products
Amazon Best Selling Products  SEO Checklist
SEO Checklist  ELECTRONIC ACCESSORIES
ELECTRONIC ACCESSORIES  Smart Doorbell
Smart Doorbell  Unreal Engine 5 For Beginners Learn The Basics Of Virtual Production
Unreal Engine 5 For Beginners Learn The Basics Of Virtual Production  Hello Theme
Hello Theme  Only For The United States
Only For The United States  NordLocker
NordLocker  Online Technology Classes
Online Technology Classes  Favorite Company (Cuelinks)
Favorite Company (Cuelinks)  Men Clothing
Men Clothing  TitTok Revolution
TitTok Revolution  Unlimited access to classes on illustration, photography, design, film, music
Unlimited access to classes on illustration, photography, design, film, music  Creative Brief For Video Shoot
Creative Brief For Video Shoot  Best Robotic Vacuum Cleaners
Best Robotic Vacuum Cleaners  ASUS Laptop
ASUS Laptop  NordVPN
NordVPN  Top Rated From Amazon
Top Rated From Amazon  The Click Engine
The Click Engine 
















