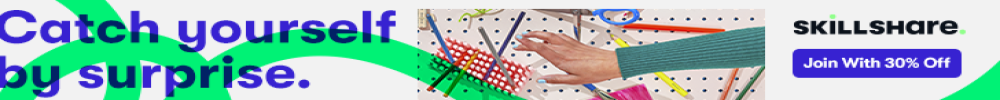
Workplace safety and injury prevention

The actions performed to ensure the health and safety of employees while they are on the job are referred to as workplace safety and injury prevention.
This entails identifying and evaluating potential workplace dangers, putting in place safety processes and regulations, giving workers the proper safety gear and training, and fostering a safety-conscious culture.
Preventing accidents and injuries, lowering the risk of occupational illnesses, and fostering a safe and healthy work environment for employees are the objectives of workplace safety and injury prevention. By increasing productivity, decreasing absenteeism, and lowering expenditures related to workplace accidents and injuries, this helps both employees and companies.
Regular safety inspections, the provision of protective gear like hard hats and safety goggles, the provision of ergonomic workstations, the implementation of safety procedures like lockout/tagout procedures for hazardous equipment, and the provision of training on how to safely operate machinery and equipment are a few examples of workplace safety and injury prevention measures.
Establishing a safety culture at work, where employees are encouraged to voice safety concerns, take part in safety training programs, and assume responsibility for their own safety as well as the safety of their coworkers, is another aspect of workplace safety and injury prevention.
Employers are required by law to create a safe workplace for their workers; failing to do so may result in penalties, legal action, and reputational harm for the business.
As a result, it's critical for employers to place a high priority on workplace safety and injury prevention by periodically identifying and resolving possible risks, giving staff members access to sufficient resources and training, and encouraging a culture of safety.
The success of the business, the productivity of the workplace, and the wellbeing of the employees all depend on workplace safety and injury prevention.
Employers may guarantee the health and safety of their workers, lower the risk of accidents and injuries, and foster a happy and productive work environment by developing and maintaining appropriate safety measures.
Employers and employees can both benefit from placing a high priority on workplace safety and injury prevention. Among these advantages are:
Employers can lower the likelihood of workplace accidents, illnesses brought on by exposure to hazardous products or circumstances, and occupational diseases by implementing safety measures and processes.
Increased productivity:
Employees are more likely to be productive and involved in their job when they feel protected and supported at work. This may result in greater productivity, better output, and lower absenteeism rates.
Lower costs:
Medical expenditures, workers' compensation claims, and missed productivity can make workplace accidents and injuries expensive for organizations. Employers can lower these expenses and increase their bottom line by putting a higher priority on worker safety.
Enhanced reputation:
A workplace that places a high priority on safety and injury prevention is seen as a responsible and ethical employer, which can improve its standing with staff members, clients, and the community.
Increased employee morale:
Employees are more likely to be content with their jobs and have higher morale when they feel safe and supported at work. This may result in lower turnover rates and higher retention.
Keeping employees safe on the job and preventing injuries are essential elements of a successful workplace. Employers can safeguard their workers, cut expenses, boost their reputation, and increase productivity by prioritizing safety and fostering a culture of safety.
Employers can prioritize workplace safety and injury prevention in a number of ways. Some of these actions consist of:
Conducting routine safety inspections:
Employers should routinely inspect the workplace for potential risks and hazards and take action to mitigate those risks.
Giving employees safety training:
Employers should give their staff safety training, which should cover handling dangerous items, using safety equipment correctly, and responding to crises.
Implementing safety protocols:
To reduce the risk of accidents and injuries, employers should implement safety protocols, such as lockout/tagout procedures for hazardous equipment.
Giving employees the proper safety gear they need, such as hard hats, safety goggles, and gloves, is the responsibility of the employer.
Establishing a safety culture:
Employers should foster a safe environment at work where employees are encouraged to voice their concerns about safety and take personal responsibility for their own and their coworkers' safety.
When employees express concerns about their safety, employers should act quickly and effectively to address those concerns and take all necessary precautions.
Employers must take a proactive approach to identifying potential risks and hazards in the workplace in order to prevent injuries.
Employers may safeguard their workers, increase productivity, improve their reputation, and increase their bottom line by prioritizing safety and fostering a culture of safety in the workplace.
Legal obligations for workplace safety and injury prevention also fall on employers.
Governments have set laws and rules in many nations to make sure that firms give their workers a safe and healthy workplace. Employers must abide with these rules and regulations, and failing to do so may result in penalties, legal action, and reputational harm to the business.
The following are a few of the legal obligations that employers may have in relation to workplace safety and accident prevention:
Creating a safe work environment:
Employers are responsible for giving their workers a place to work that is free from known risks that could lead to disease or injury.
Regular workplace safety inspections must be carried out by employers in order to spot possible dangers and take action to mitigate them.
Giving employees safety training:
Employers are obligated to give workers safety training, which includes instruction on how to utilize safety gear, handle dangerous products, and react to crises.
Keeping safety records:
Employers are expected to keep track of any illnesses or injuries that occur on the job and to report them to the appropriate government agencies.
Responding to safety complaints:
Employers are obligated to take action to remedy any hazards or risks that are discovered as well as respond promptly and appropriately to any safety complaints made by employees.
In general, companies have a moral and legal obligation to put workplace safety and harm prevention first. Employers may safeguard their workers, cut expenses, improve their reputation, and increase their bottom line by adhering to laws and regulations relating to workplace safety and fostering a culture of safety in the workplace.
Additionally, it is the duty of employees to put workplace safety and injury prevention first. Employees are expected to adhere to the safety rules and regulations set forth by their employers and to take precautions to keep both themselves and their coworkers safe.
Employees may be expected to perform the following duties in relation to workplace safety and injury prevention:
Following safety protocols:
Employees are expected to adhere to the policies and guidelines for safety set forth by their employers, such as donning the proper protective gear and reporting any safety issues.
Participating in safety training:
Employees are required to attend safety training sessions offered by their employers and to use the knowledge and skills they acquire in these sessions in their regular job.
Safety issues and hazards should be reported to supervisors or safety representatives by employees, who should also take action to eliminate any risks or hazards that are found.
Employees are required to take ownership of their own safety as well as the safety of their coworkers by adhering to safety procedures, notifying management of any concerns, and utilizing safety equipment as directed.
Coordination with coworkers is required in order to make sure that safety rules and procedures are followed and to take action in response to any dangers or risks that may be found.
In order to ensure workplace safety and accident prevention, employees are essential.
Employees can contribute to a safe and effective workplace by adhering to safety standards and procedures, reporting safety issues, and taking personal responsibility for their own safety as well as the safety of their coworkers.
Governmental organizations also have a part to play in workplace safety and injury prevention, in addition to companies and workers. Governments enact rules and regulations, and they could also offer resources and assistance for workplace safety programs, to make sure that firms give their workers a safe and healthy working environment.
Governmental organizations may participate in workplace safety and injury prevention in a number of ways, including:
Creating rules and regulations:
Governments have the authority to create laws and regulations that pertain to workplace safety, such as those that specify the usage of safety equipment and the need for safety training, as well as the consequences for breaking them.
Governments may give financing for research and development of new safety technologies as well as training and education programs for both employers and employees as part of their support for workplace safety efforts.
Inspections and investigations:
To verify that safety laws and regulations are being followed and to identify potential dangers and risks to the health and safety of employees, governments may examine and investigate workplaces.
Enforcing safety laws and regulations:
Governments have the authority to take legal action against employers who violate safety regulations and impose fines, penalties, or both.
By formulating laws and regulations, providing resources and support, conducting inspections and investigations, and enforcing safety standards, government agencies play a significant role in maintaining workplace safety and accident prevention. Government organizations can contribute to the creation of a safer and healthier working environment for everyone by collaborating with employers and workers.
Risk assessment is a crucial component of occupational safety and harm prevention.
Finding potential risks and hazards at work, assessing the likelihood and seriousness of harm, and taking action to reduce or eliminate those risks are all part of the risk assessment process.
The following are a few possible steps in risk assessment:
To detect potential risks and hazards in the workplace, such as machinery, chemicals, or other physical or environmental dangers, employers may undertake a hazard assessment.
Employers can assess the probability and seriousness of harm that might be caused by each potential hazard by employing instruments like risk matrices or hazard analysis.
Creating risk management strategies:
Based on the findings of the hazard assessment, companies may create risk management plans to reduce or get rid of the hazards that were found. These plans can include modifying equipment, altering work procedures, or adding more safety gear or training.
Employers can put the risk management plans created in the previous stage into practice by adding safety guards to machines, outfitting workers with protective gear, or changing work procedures to lessen exposure to dangers.
Monitoring and evaluating risk management tactics:
Employers can keep an eye on the efficiency of their risk management tactics and alter them as needed to maintain workplace safety.
In general, risk assessment is an important part of workplace safety and injury prevention and can assist companies in identifying and removing possible risks before they hurt workers. Employers may make their workplaces safer and healthier for everyone by conducting regular risk assessments and putting in place efficient risk management strategies.
To understand the value of cooperation and communication in preventing accidents and maintaining workplace safety.
To identify possible dangers, create and implement risk management plans, and make sure that safety regulations and procedures are followed, employers, employees, and governmental organizations must collaborate.
Collaboration and effective communication might involve:
Regular safety meetings: Employers may arrange regular safety meetings to go over safety guidelines and procedures, talk about potential risks, and offer training and information on workplace safety.
Safety protocols and procedures should be communicated to employees in a clear and understandable manner. Employers should also train and educate staff members on how to follow these policies.
Open channels of communication between employees and management:
Employees should feel at ease approaching their supervisors or safety representatives with concerns about potential dangers, and employers should be receptive to these concerns and take action to resolve them.
Collaboration between businesses, workers, and governmental organizations:
Employers, workers, and governmental organizations should collaborate to identify and address workplace safety issues, share knowledge and materials, and create and put into practice efficient risk management plans.
Employers, workers, and government organizations can cooperate to develop a work environment that is safer and healthier for everyone by putting a priority on good communication and collaboration.
Any successful firm must prioritize workplace safety and injury avoidance.
Employees have a responsibility to follow safety rules and procedures to protect their own safety and the safety of their coworkers, and employers have a responsibility to offer a safe and healthy work environment for their employees.
Employers can take a number of actions to ensure workplace safety and injury prevention, including conducting risk assessments, offering safety training and education, putting effective risk management strategies into place, and promoting open communication and collaboration between staff and management. The establishment of laws and regulations, the provision of resources and support, the execution of inspections and investigations, and the enforcement of safety requirements are all important functions performed by government organizations.
Employers, workers, and governmental organizations must collaborate to identify and eliminate potential hazards, create and implement efficient risk management plans, and place a high priority on everyone's safety and wellbeing at work in order to successfully prevent workplace injuries.














 Unreal Engine 5 For Beginners Learn The Basics Of Virtual Production
Unreal Engine 5 For Beginners Learn The Basics Of Virtual Production  Favorite Company (Cuelinks)
Favorite Company (Cuelinks)  ASUS Laptop
ASUS Laptop  Artificial Intelligence
Artificial Intelligence  NordLocker
NordLocker  Graphics & Design
Graphics & Design  Hello Theme
Hello Theme  Men Clothing
Men Clothing  SOFAS
SOFAS  Smart Doorbell
Smart Doorbell  NordPass
NordPass  Top Rated From Amazon
Top Rated From Amazon  One World Collection
One World Collection  1150+Trendy kids coloring pages Bundle
1150+Trendy kids coloring pages Bundle  RPM 3.0
RPM 3.0  NordVPN
NordVPN  Women Fashion
Women Fashion  Unlimited access to classes on illustration, photography, design, film, music
Unlimited access to classes on illustration, photography, design, film, music  Acer Laptop
Acer Laptop  BEST SELLER TOP10
BEST SELLER TOP10  ELECTRONIC ACCESSORIES
ELECTRONIC ACCESSORIES  ASPINAL LONDON
ASPINAL LONDON  Sennheiser
Sennheiser  Hot Bags For Pain Relief
Hot Bags For Pain Relief  Amazon Best Selling Products
Amazon Best Selling Products  Best Home Appliances
Best Home Appliances  All Wireless Products
All Wireless Products  Best Selling Books
Best Selling Books  Online Technology Classes
Online Technology Classes  SEO Checklist
SEO Checklist  Online Marketing
Online Marketing  Creative Brief For Video Shoot
Creative Brief For Video Shoot  The Secret Email System
The Secret Email System  Best Robotic Vacuum Cleaners
Best Robotic Vacuum Cleaners  Best Sellers On Amazon
Best Sellers On Amazon  TitTok Revolution
TitTok Revolution  The Click Engine
The Click Engine  Only For The United States
Only For The United States